This page contains links to utility programs related to coordinate measuring machines and inspection. The utility programs are purpose specific and were written as needed. Utility programs are compiled for various operating systems and available as source code where practical.
All programs with a GUI interface are written using the Qt Framework. To compile any of these programs it is necessary to download and install the Qt SDK for your target operating system. The license for the community editions of Qt are LGPL and GPL.
These programs are free software: you can redistribute and/or modify them under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. All software is provided as-is; no warranty of any kind is provided or implied.
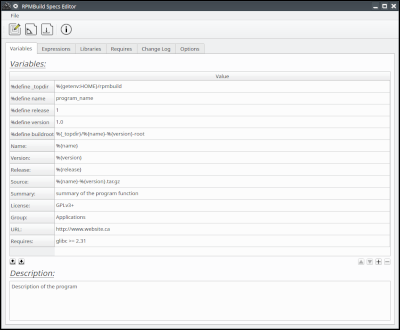
The RPMSpecsEditor utility allows the user to create a SPEC file that is read by the RPMBuild utility in order to create an RPM file. An RPM file is a package format used by the RPM Package Manager, primarily for installing software on GNU/Linux distributions such as Red Hat, Fedora, SUSE Linux, and CentOS. The RPMSpecsEditor is geared toward Qt applications containing various libraries and plugins but should be adaptable to other frameworks if needed.
| Linux RPM: | rpmspecseditor-1.4-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Source: | rpmspecseditor-1.4.src.zip |
| Doc: | RPMSpecsEditor Users Guide.pdf |
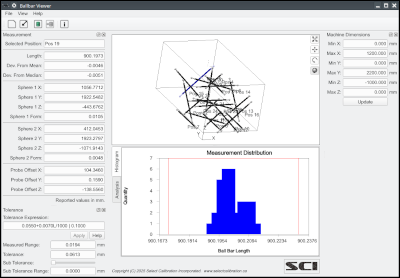
The Ballbar Viewer allows users to analyze ball bar measurement data when performing interim checks on their CMM. Interim checks are necessary to ensure that the CMM is measuring properly and can also be used to verify changes to the machine, such as a software upgrade, have not adversely affected accuracy.
| Linux RPM: | ballbarviewer-5.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | ballbarviewer_5.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | ballbarviewer-5.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | ballbarviewer-5.1.src.zip |
| Part Program: | B89.4.1-Ballbar-V8.2-PCD37.PRG.zip |
| Doc: | Ballbar Viewer Users Guide.pdf |
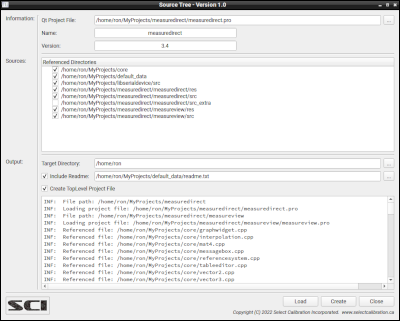
The Sourcetree utility creates a folder populated with all files and dependent projects necessary to compile a specific Qt project. The created folder can then be compressed and distributed as the source code for the Qt project. The generated source tree optionally includes a top-level project file and compilation instructions. Starting with version 2.0 of the Sourcetree utility the cmake CMakeLists.txt files are automatically generated from all Qt project files allowing makefiles to be created from QMake or CMake depending on user preferences.
| Linux RPM: | sourcetree-2.3-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | sourcetree_2.3-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | sourcetree-2.3-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | sourcetree-2.3.src.zip |
| Doc: | Sourcetree Users Guide.pdf |
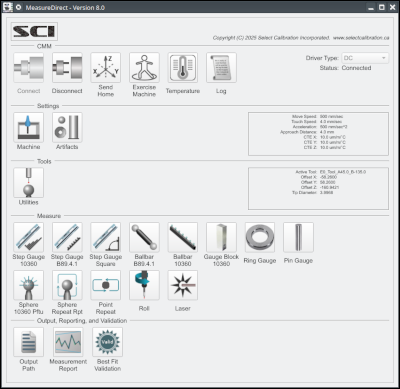
The MeasureDirect utility is inspection software with a very narrow scope of capability focusing on the measurement of artifacts for CMM calibration. MeasureDirect can perform measurement tests using a step gauge, gauge block, ring gauge, pin gauge, sphere, B89.4.1 or 10360 ball bar, and laser.
| Linux RPM: | measuredirect-9.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | measuredirect_9.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | measuredirect-9.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | measuredirect-9.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | MeasureDirect Users Guide.pdf |
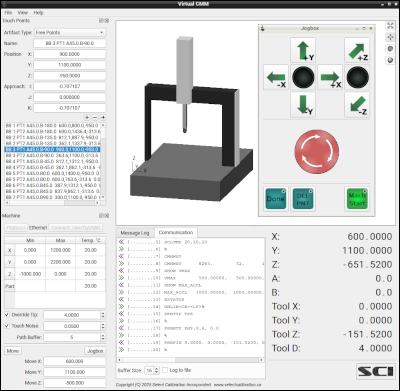
VirtualCMM is software that emulates the functions of a physical CMM. It was written primarily for testing the measurement routines of MeasureDirect when an actual CMM is not available. The virtual machine is animated and can display the recent probe path to help identify problems such as missing moves or inverted touch points.
| Linux RPM: | virtualcmm-8.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | virtualcmm_8.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | virtualcmm-8.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | virtualcmm-8.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | VirtualCMM Users Guide.pdf |
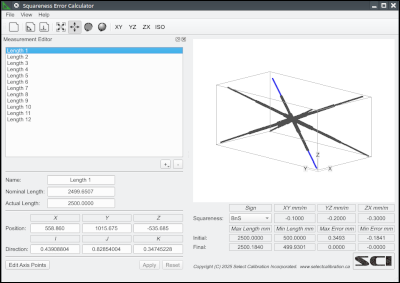
The Squareness Error Calculator is a utility that can find the ideal squareness corrections from a set of length measurements on a CMM. The measurements of length can be from a ball bar or from artifacts such as step gauges, gauge blocks, or a laser interferometer. The sample measurement data supplied with this utility has examples of each type and has been somewhat randomized to demonstrate the capabilities of the Squareness Error Calculator.
| Linux RPM: | squarenesscalculator-3.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | squarenesscalculator_3.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | squarenesscalculator-3.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Sample Data: | sq_sample_data.zip |
| Doc: | Squareness Calculator Users Guide.pdf |
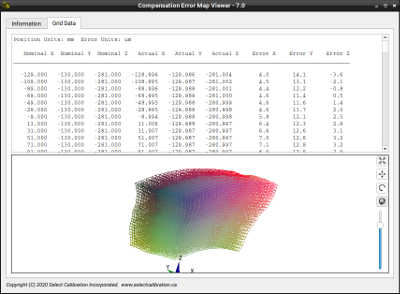
The Compensation Map Viewer was written to allow users to view the contents of the error map or error grid from their CMM. The data is presented as a text table of values and select parameters can be displayed graphically if desired. Any supported map type can be opened by simply dragging the file onto the Compensation Viewer program. Many file formats from a variety of vendors can be opened by this program.
This program will not pull data from the CMM controller. The compensation map must exist as a file (or a folder containing individual compensation parameters) to be able to use this utility.
| Linux RPM: | compview-9.2-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | compview_9.2-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | compview-9.2-1.x86_64.zip |
| Doc: | Compview Users Guide.pdf |
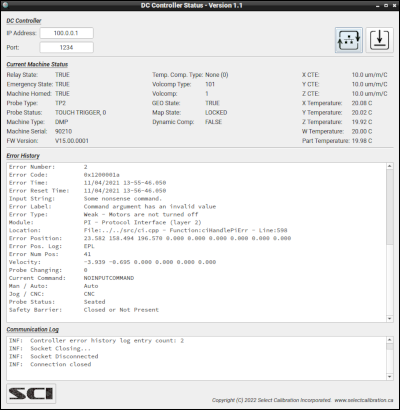
The DC Controller Status utility shows current information about the CMM along with recent errors logged by the controller. The current information shows the emergency status, error map compensation configuration, axis expansion coefficients, and axis temperatures. The error log shows the history of errors recorded by the controller since the last reboot. The data can be recorded and saved to a text file with minimal effort from the user.
| Linux RPM: | dccontrollerstatus-1.3-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | dccontrollerstatus_1.3-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | dccontrollerstatus-1.3-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | dccontrollerstatus-1.3.src.zip |
| Doc: | DC Controller Status Users Guide.pdf |
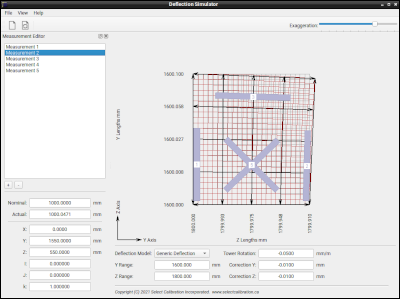
The Deflection Simulator shows the effect of deflection compensation from different vendors on a horizontal arm CMM with a kinematic of XZY. The input parameters for the different deflection models match those of the vendor and the output shows a series of horizontal and vertical length measurements that would be observed with a laser. Measurement gauges can be added anywhere inside the measurement volume in order to see the impact on length.
| Linux RPM: | deflectionsimulator-2.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | deflectionsimulator_2.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | deflectionsimulator-2.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | deflectionsimulator-2.1.src.zip |
| Doc: | Deflection Simulator Users Guide.pdf |
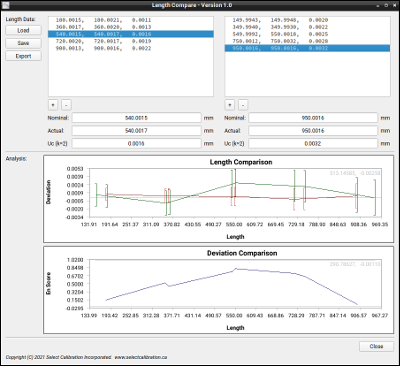
The Length Compare utility calculates a series of En score values from two sets of overlapping length measurements as part of the interim testing process. The En score is one method to compare measurements by combining the deviation with the measurement uncertainty.
| Linux RPM: | lengthcompare-2.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | lengthcompare_2.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | lengthcompare-2.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | lengthcompare-2.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | Length Compare Users Guide.pdf |
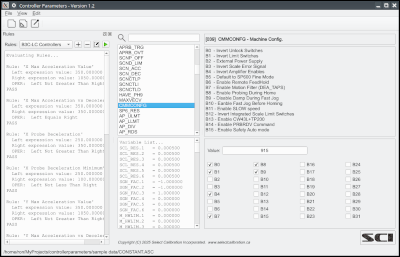
The Controller Parameters utility was written to allow viewing or editing the contents of parameter files used by Common Controllers (FBPC, FB2, B3C-LC, …) or DC controllers (DC800, DC240, DC241, RC1, ...). The modified parameters can be exported to a text file then manually merged into the original parameter file.
Parameters can be validated using a set of parameter rules. The parameter rules can be used to validate any parameter against a constant or expression product from any other parameter or combination of parameters.
| Linux RPM: | controllerparameters-1.2-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | controllerparameters_1.2-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | controllerparameters-1.2-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | controllerparameters-1.2.src.zip |
| Doc: | Controller Parameters User Guide.pdf |
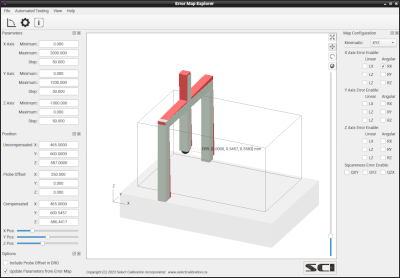
The Error Map Explorer is a utility that can calculate corrections based on data from a compensation error map and produce numerical and graphical results. The correction values are calculated to the position of the active tool stylus tip and is comparable to methods used by most CMM's.
The Error Map Explorer can load compensation data from a variety of sources. The sample error map file is provided with this utility can be used if access to map data is not available. A sample test sequence file is also available in order to demonstrate the capabilities.
| Linux RPM: | errormapexplorer-4.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | errormapexplorer_4.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | errormapexplorer-4.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Sample Data: | Error_Map_And_Test_Sequence.zip |
| Doc: | Error Map Explorer Users Guide.pdf |
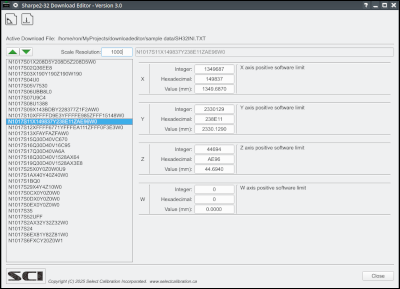
The download editor was written to allow direct modification of the Sharpe2-32 download files. The normal method for modification of these files is to change the master parameter data then generate a new download file for the controller. Since these files are frequently not available this editor was created to allow more direct access to the download file.
| Linux RPM: | downloadeditor-3.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | downloadeditor_3.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | downloadeditor-3.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | downloadeditor-3.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | Download Editor Users Guide.pdf |
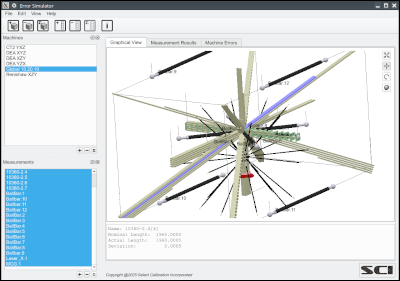
The Error Simulator utility allows simulated CMM measurements of various artifacts in order to assist in the development of tools and procedures necessary for efficient calibration of coordinate measuring machines. Developing methods to extract specific machine errors from measurements require accurate test data so that methods can be evaluated properly. Using a real CMM can be problematic as physically changing the shape of the machine in order to test different scenarios is not possible in many cases and measurement noise can also bias data.
| Linux RPM: | errorsimulator-5.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | errorsimulator_5.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | errorsimulator-5.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | errorsimulator-5.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | Error Simulator Users Guide.pdf |
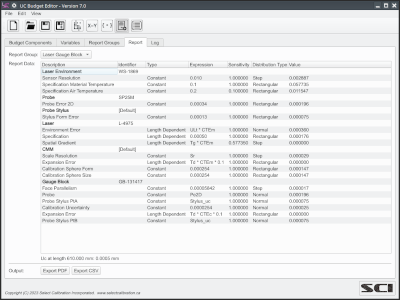
The UCBudget Editor is a utility for creating or editing uncertainty budget data and is intended to be used as the basis of an uncertainty budget for one or more measurements. The utility was written around the idea of a coordinate measuring machine but can be applied to other equipment. The uncertainty budget data file can be used by other software for automatic calculation of uncertainty values.
| Linux RPM: | ucbudgeteditor-9.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | ucbudgeteditor_9.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | ucbudgeteditor-9.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | ucbudgeteditor-9.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | UCBudget Editor Users Guide.pdf |
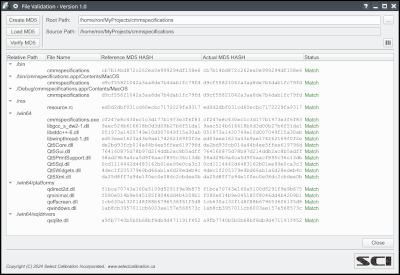
The Validation utility creates a set of MD5 hash values from one or more files which can be used to determine if the contents or those files change in the future. The reference hash for each file is created from a set of trusted sources and used to compare to the same files at some future point in time.
Changes can be the result of file system corruption or from direct modification by a virus or malware running on an un-trusted computer. File system corruption can happen when files are installed on a USB drive as these are typically formatted with FAT32 and do not have any kind of activity journal. USB drives can be removed without being properly ejected which can lead to file system corruption.
| Linux RPM: | validation-1.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | validation_1.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | validation-1.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | validation-1.1.src.zip |
| Doc: | Validation Users Guide.pdf |
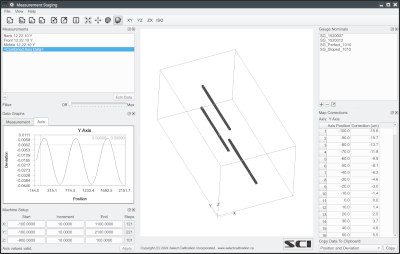
The Measurement Staging utility allows the user to combine two or more step gauge measurements along a machine axis and generate a set of corrections that can be directly added to the existing compensation map data. Combining two or more step gauge measurements is common when mapping a machine axis when the machine axis length is significantly longer then that of the step gauge. The approach used by the Measurement Staging utility prefers measurements that overlap each other but measurements in opposite directions or even measurements with gaps between the positions are acceptable inputs. The individual positions can be filtered to help clean up effects of measurement noise on the data.
| Linux RPM: | measurementstaging-1.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | measurementstaging_1.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | measurementstaging-1.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | measurementstaging-1.1.src.zip |
| Sample Data: | ms_sample_data.zip |
| Doc: | Measurement Staging Users Guide.pdf |
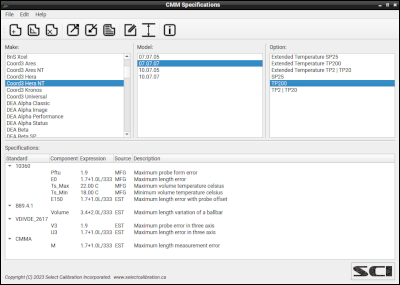
The CMM Specifications utility allows the user to access the limits for various brands and models of CMM’s when running performance tests of the machine as defined by standards such as ISO/IEC 10360-2:2009. The information is stored in a SQLite database and can be converted to a CSV file for importing or exporting as needed.
The sample database has publicly available specifications for various CMM's collected over the years. Although there has been a lot of effort to keep the information correct it is highly probable that some of the data is not valid for various reasons. Additions or revisions are welcome and the sample database on the website will be updated to contain the latest information.
| Linux RPM: | cmmspecifications-1.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | cmmspecifications_1.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | cmmspecifications-1.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | cmmspecifications-1.1.src.zip |
| Database: | cmmspecifications.db.zip |
| Doc: | CMM Specifications Users Guide.pdf |
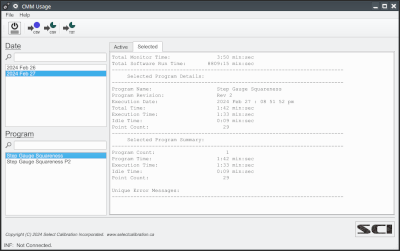
The CMMUsage utility allows collection of usage data from the CMM software focusing on run time, idle time, and off time. In addition to usage data the touch trigger point count and any errors reported by the controller are recorded and can be reviewed for troubleshooting purposes. The data is stored in a SQLite database and can be accessed directly from any suitable software or exported to a CSV or text file from the CMMUsage utility for review.
The recorded error messages and touch trigger probe count may be of particular use. As often the case intermittent errors are not always recorded by the user but, with this utility, the date, time, program name, and text of the error message is saved and can be reviewed at a later date. The touch trigger probes have a finite lifespan based on the number of touches. Using a sample of typical usage data it would be possible to estimate when the limit of touches has been reached.
| Windows: | cmmusage-1.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | cmmusage-1.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | CMMUsage Users Guide.pdf |
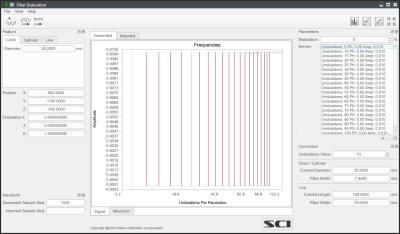
The Filter Evaluation utility allows the user to generate test data with specific signals in order to evaluate the inspection software’s ability to filter the test data. One observation, particularly noticed when writing this utility, is how vague the various options provided by the inspection software can be. Using this utility allows a better understand the capability of the inspection software and the impact of various filter settings.
| Linux RPM: | filterevaluation-1.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | filterevaluation_1.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | filterevaluation-1.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | filterevaluation-1.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | FilterEvaluation Users Guide.pdf |
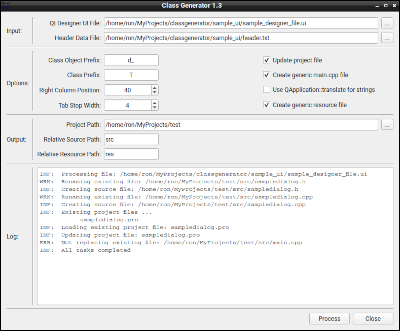
The ClassGenerator utility converts the Qt Designer UI forms into standard C++ source and header files. This program was written to simplify the process used by the author to create source files from the Qt Designer UI file for GUI elements. The difference between the output created by this utility and the output produced by Qt version is that the ClassGenerator version is more focused on creating traditional C++ source and header files. The downside when using this method is that revisions of the UI forms are difficult to incorporate into existing programs.
| Linux RPM: | classgenerator-1.3-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | classgenerator_1.3-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | classgenerator-1.3-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | classgenerator-1.3.src.zip |
| Sample: | sample_designer_file.ui.zip |
| Doc: | ClassGenerator Users Guide.pdf |
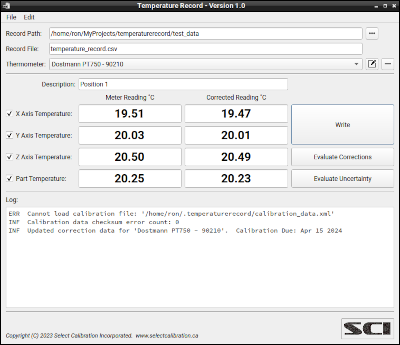
The Temperature Record utility allows the user to create a record file of one or more measured temperatures and to compensate for known thermometer errors based on three data points. The correction is based on a curve touching the three calibration temperature points that may or may not be linear resulting in a more natural shape as compared to a straight-line approximation between any two of the three points. Utilities are included to assist in evaluation and estimation of measurement uncertainty. Calibration data can be setup for more than one thermometer. No support for imperial (Fahrenheit) temperatures is provided with this utility.
| Linux RPM: | temperaturerecord-1.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | temperaturerecord_1.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | temperaturerecord-1.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | temperaturerecord-1.1.src.zip |
| Doc: | Temperature Record Users Guide.pdf |
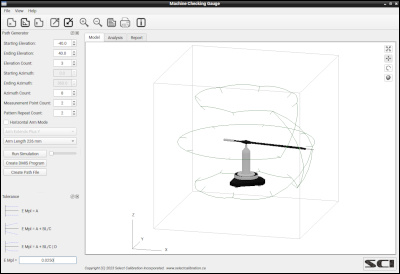
The Machine Checking Gauge utility is software that compliments the Renishaw MCG test artifact. The primary purpose of the Machine Checking Gauge utility is to interpret and report data collected by the Renishaw MCG artifact but it can also be used to create a part program necessary for the measurement of the gauge.
| Linux RPM: | mcg-4.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | mcg_4.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | mcg-4.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | mcg-4.0.src.zip |
| Part Program: | MCG - 3.0 - PC-DMIS 3.7.PRG.zip |
| Doc: | Machine Checking Gauge Users Guide.pdf |
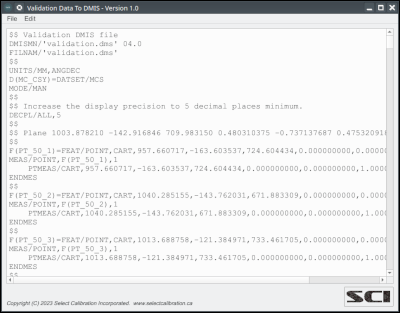
The Validation2DMIS utility creates a DMIS part program based on the validation data from MeasureDirect. The DMIS program contains the point data and constructed features of the type specified in the validation data file. Creation of a DMIS program from the validation data allows importing into any software that supports the DMIS standard.
| Linux RPM: | validation2dmis-1.0-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | validation2dmis_1.0-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | validation2dmis-1.0-1.x86_64.zip |
| Source: | validation2dmis-1.0.src.zip |
| Doc: | Validation2DMIS Users Guide.pdf |
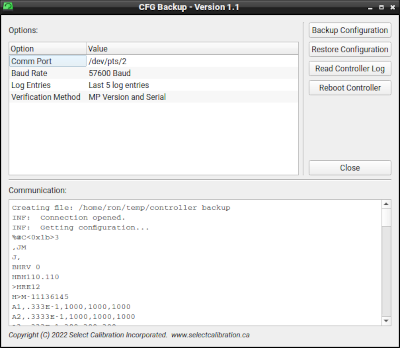
CFGBackup utility allows the user to backup and restore the CMM controller EEProm data from various Sheffield brand CMM's.
Under normal conditions the EEProm data in the controller is stable and does not change unless specifically written but due to age or other factors the EEProm data can change randomly particularly following a cycle of the controller power. The controller performs a CRC error check on the EEProms at power-up and if this fails (meaning the contents of the EEProms does not match the previous known values) then the controller is put into a permanent error state until fixed. The CFGBackup utility allows the user to create a backup file containing a copy of all the controller's EEProm data and restore it on a future date in order to clear any CRC error that may happen.
| Linux RPM: | cfgbackup-1.1-1.x86_64.rpm |
| Linux DEB: | cfgbackup_1.1-2_amd64.deb |
| Windows: | cfgbackup-1.1-1.x86_64.zip |
| Doc: | CFGBackup Users Guide.pdf |